October 30, 2025
Announcing Rspack 1.6

We are excited to announce Rspack 1.6!
Notable changes include:
- New Features
- Rstack Progress
- Ecosystem
New features
Enhanced tree shaking
Rspack 1.6 improved tree shaking support for dynamic imports. In previous versions, Rspack could only perform tree shaking on destructured assignments within dynamic imports, while other import patterns were not analyzed.
Now, Rspack introduces comprehensive static analysis for dynamic imports. It can recognize and handle a wider range of usage patterns. This allows Rspack to precisely eliminate unused exports and further reduce the size of the final bundle.
Support for import defer
Rspack now supports the import defer syntax.
import defer is a new feature in JavaScript, which is also supported in TypeScript 5.9. It allows you to import a module without immediately executing the module and its dependencies, giving you better control over when code execution and side effects occur.
You can enable this feature through experiments.deferImport:
Currently, Rspack only supports the
import defersyntax. The function formimport.defer()will be implemented in future versions.
Improved ESM output
Optimizing ESM output has long been one of the key challenges faced by Rspack. Previously, we relied on module concatenation to optimize ESM outputs, but that approach had several limitations:
- Impure output – The generated files contained Rspack's runtime code.
- Prone to errors – Some modules could not be correctly concatenated, leading to unexpected runtime issues.
- Limited code-splitting support – Split bundles became complex and difficult to analyze or optimize statically.
To address these issues once and for all, we introduced an experimental plugin called EsmLibraryPlugin, purpose-built for constructing clean and efficient ESM libraries:
- Full control over the bundling process – All modules are linked during compilation, eliminating reliance on Rspack's runtime.
- Code-splitting support – Code after splitting can be statically analyzed and is tree-shaking friendly.
The image below compares the code splitting output before and after using this plugin — the left side shows the previous output, while the right side shows the cleaner output produced by EsmLibraryPlugin:
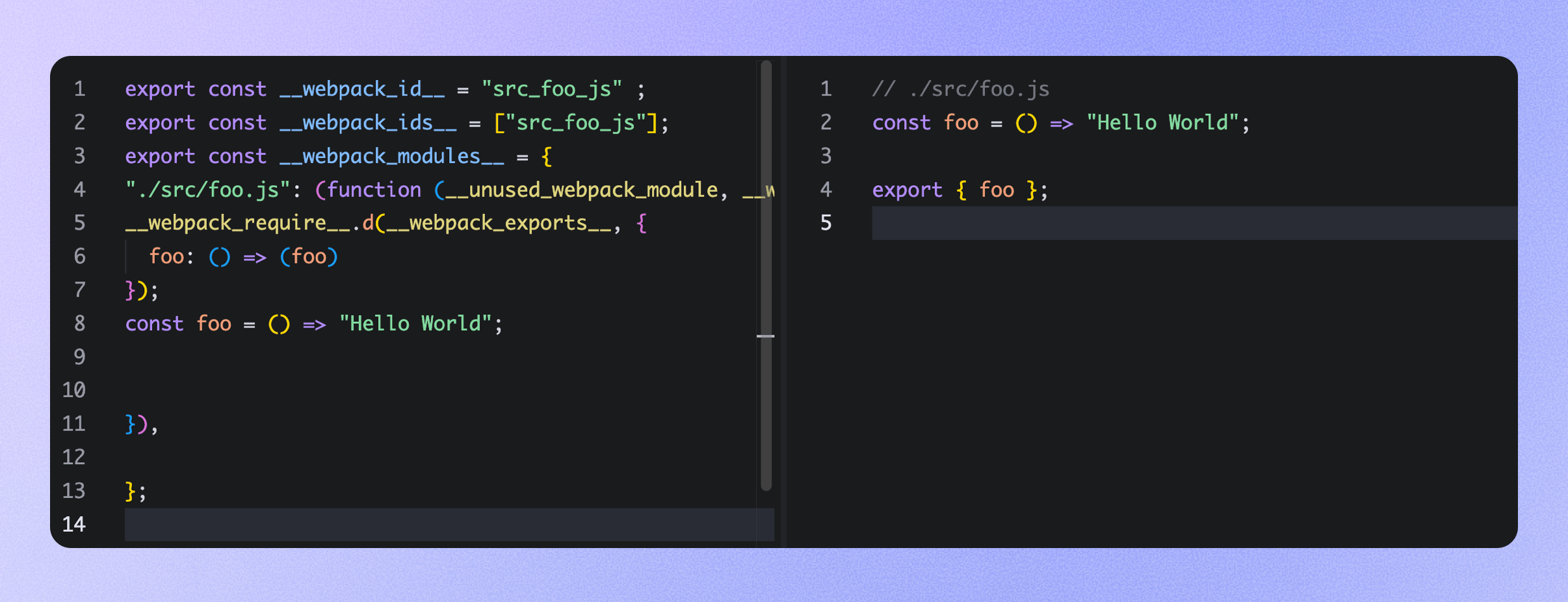
The EsmLibraryPlugin is now largely complete and is being integrated into Rslib to provide an out-of-the-box experience. You can also enable it manually with the following configuration:
In addition, we've introduced an preserveModules option that preserves the original directory structure of your source files in the output:
Optimized barrels by default
In Rspack 1.5, we introduced the experimental lazyBarrel optimization feature, specifically designed to improve the build performance of barrel files. After a period of production environment practice and user feedback collection, we confirmed that the lazyBarrel feature has reached a stable state, so it is enabled by default in Rspack 1.6.
What are barrel files? Barrel files are files that are primarily used to re-export content from other modules, typically used to simplify import paths and provide a unified API entry point.
Stabilized layers feature
Layer is a feature for organizing modules into different layers, which can be useful in advanced scenarios such as React Server Components. By assigning different layers to modules, you can gain finer control over their build behavior, for example:
- Compiling modules in different layers for different target environments
- Outputting them to separate build directories
Starting from Rspack 1.6, the layer feature has become stable enough that the experimental flag experiments.layers has been deprecated. You can now use the layer feature directly without the experimental flag.
For more details and practical examples, check out our new Layer guide.
Preserve JSX syntax
Rspack now supports preserving JSX syntax in the build output. When this option is enabled, Rspack only parses JSX syntax without transforming it into JavaScript.
This feature is especially useful when building libraries that rely on JSX. For example, when using Rslib to build a component library, you can choose to keep the JSX code as-is in the output, allowing the consumer to handle the final JSX transformation during usage.
Extract source map
Rspack now supports extracting existing source map data from files (from their //# sourceMappingURL comments) through rules[].extractSourceMap. This feature is particularly useful for preserving source maps provided by third-party libraries, ensuring that debugging information remains accurate even when these libraries are bundled or transformed.
This feature was introduced as a built-in alternative to source-map-loader, providing better performance and tighter integration with the build process.
Performance improvements
Rspack 1.6 introduces several performance optimizations. Compared with Rspack 1.5.0, you can expect the following improvements:
- CLI startup is about 50 ms faster
- Building 10000 React components is 11% faster
- Building multiple UI component libraries is 31% faster (thanks to the newly enabled barrel-file optimization by default)
Data source: Rspack benchmark
Rstack progress
Rstack is a unified JavaScript toolchain centered around Rspack, featuring excellent performance and consistent architecture.
Rsbuild 1.6
Forward browser logs
Rsbuild now automatically forwards error logs from the browser to the terminal, helping you conveniently view runtime errors during development. This also enables Coding Agents to obtain more complete context from terminal logs, allowing them to better analyze and locate errors.
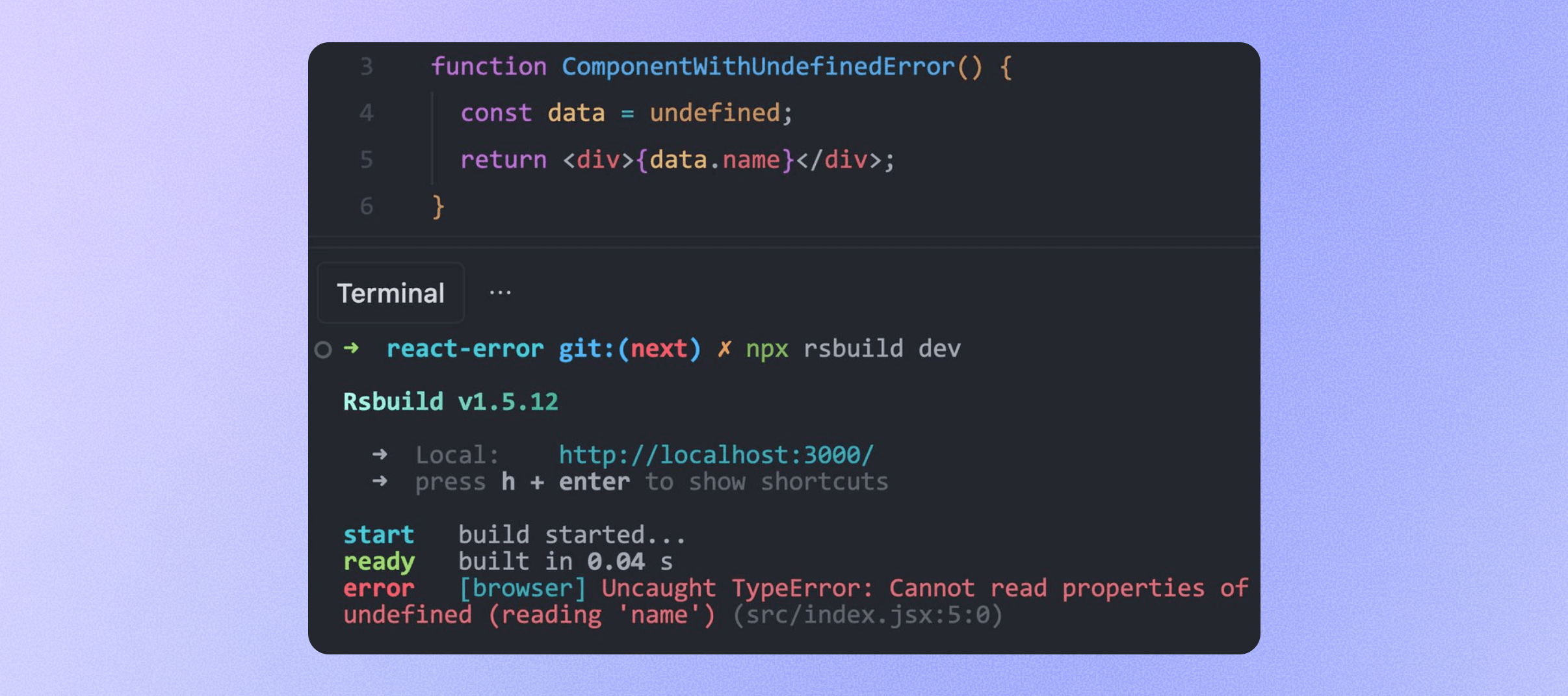
If you don't need this feature, you can disable it by setting dev.browserLogs to false:
Building ESM applications
Rsbuild now supports building ES Modules format output for Web applications, simply enable output.module: true:
Once enabled, Rsbuild will no longer generate IIFE format scripts by default, but will output standard ESM format and automatically set the generated <script> tags to type="module".
Faster configuration loading
Since Node.js 22 already natively supports TypeScript, Rsbuild now defaults to using Node.js's native loader to parse configuration files; if loading fails, it will automatically fall back to Jiti. When using Node.js 22 and above, this mechanism ensures that module resolution behavior remains consistent with Node.js native behavior while providing better loading performance.
You can also manually specify the loading method through the Rsbuild CLI's --config-loader option:
Rspress v2 beta
New theme preview
Rspress's new theme has entered preview phase and is now live on the v2 website. 🎉
The new theme has been comprehensively upgraded in design, bringing a better documentation reading experience. It also exposes more theme APIs and CSS class names, making it easier for developers to customize the UI.
👉 Visit the Rspress v2 website to try it out.
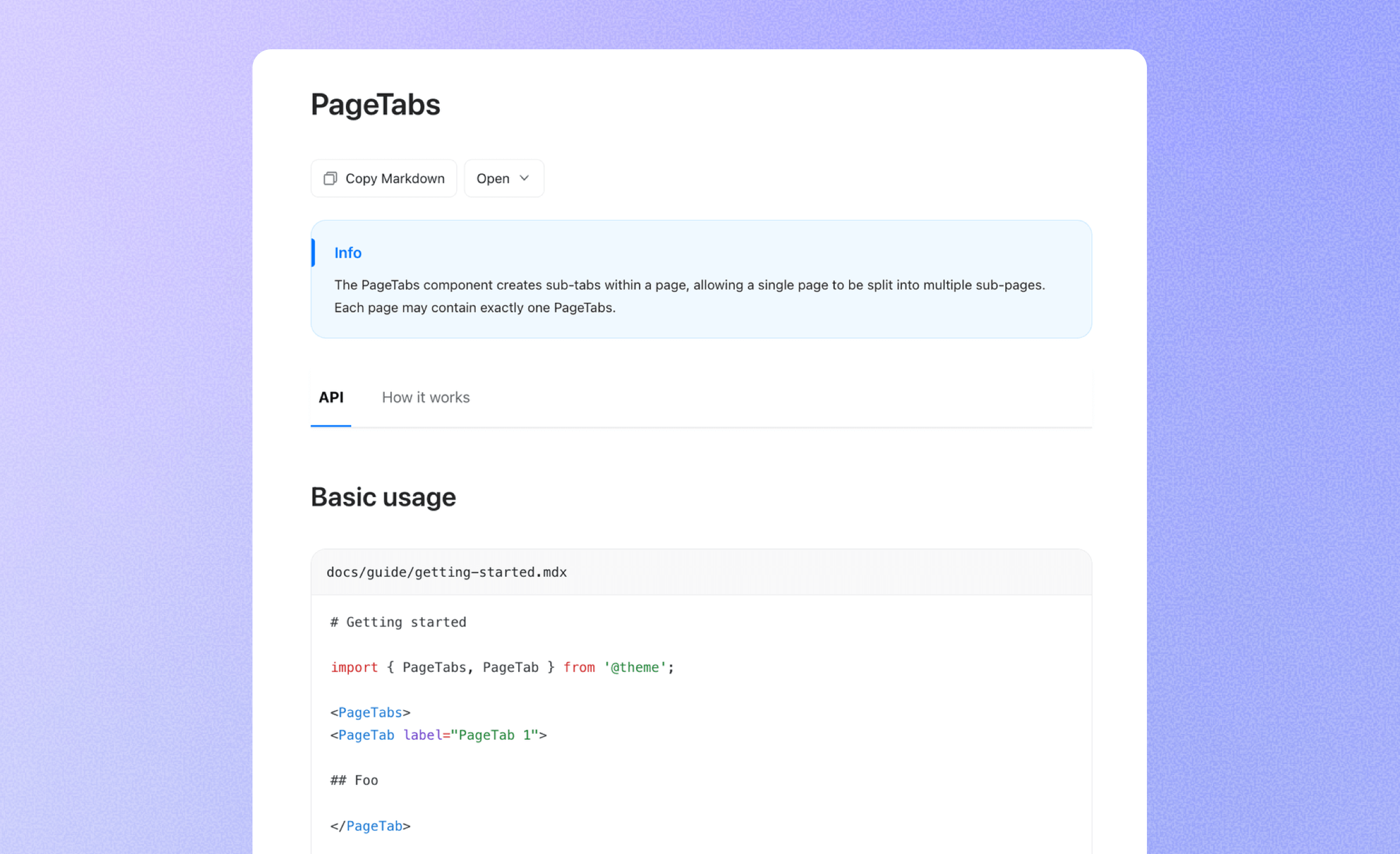
Sub-page switching
Rspress v2 introduces the PageTabs component, allowing you to create multiple sub-tabs within a single page. This helps naturally split long content into well-structured subpages.
Rslib 0.16
Faster type generation
Rslib now supports generating type declaration files based on typescript-go. By simply enabling dts.tsgo, you can boost type checking and declaration generation performance by around 300%, with even greater benefits in large projects.
Preserve JSX syntax
Rslib now supports preserving original JSX in build output, simply set runtime to 'preserve'. In this mode, JSX syntax will be preserved as-is without any transformation, making it convenient for subsequent processing by other bundling tools.
More CLI options
Rslib supports additional CLI options in the build command, which take precedence over configuration files.
This also allows you to use Rslib without a configuration file, and the CLI will automatically use a default configuration containing only a single lib and complete the build based on command line parameters.
Rstest 0.6
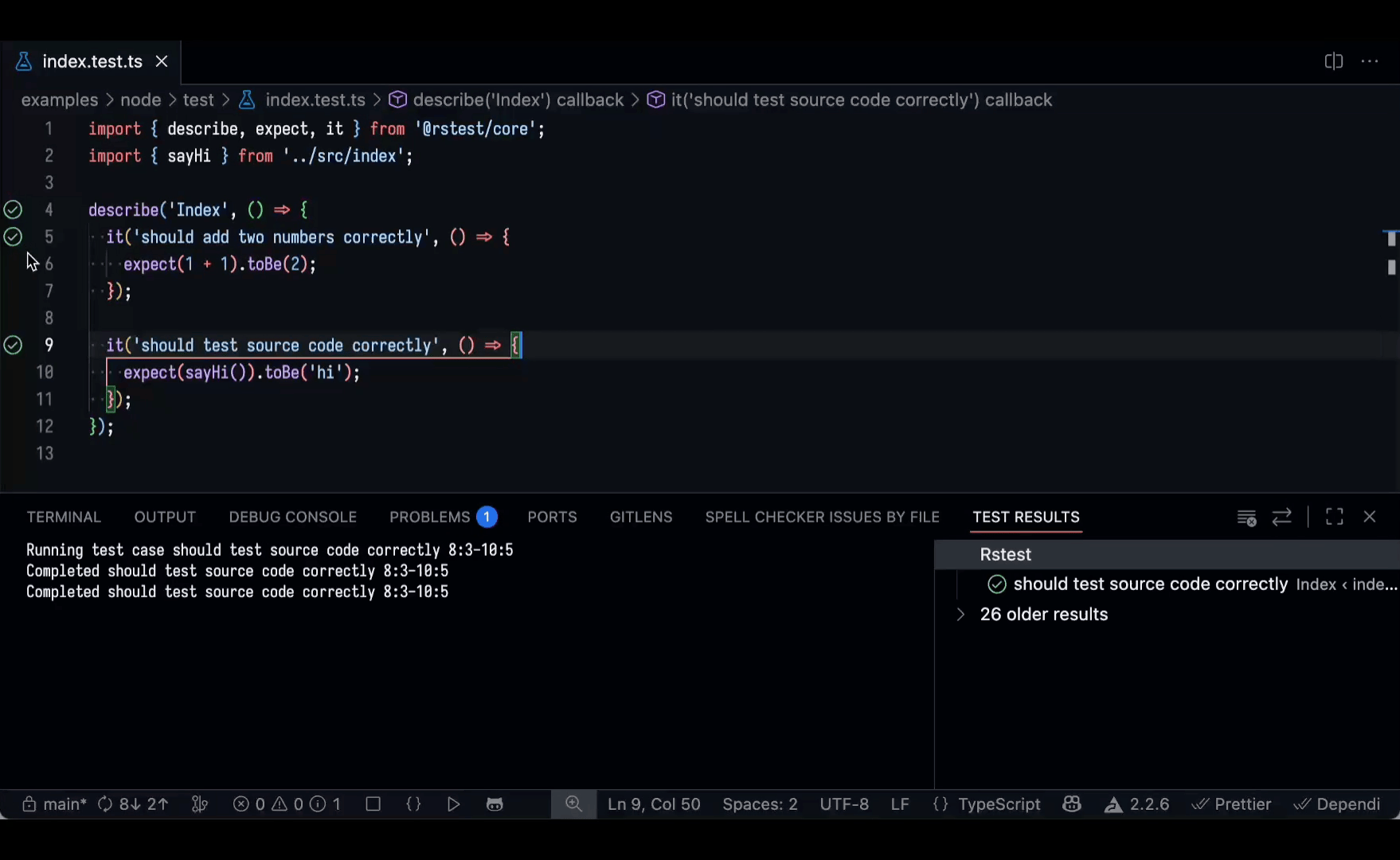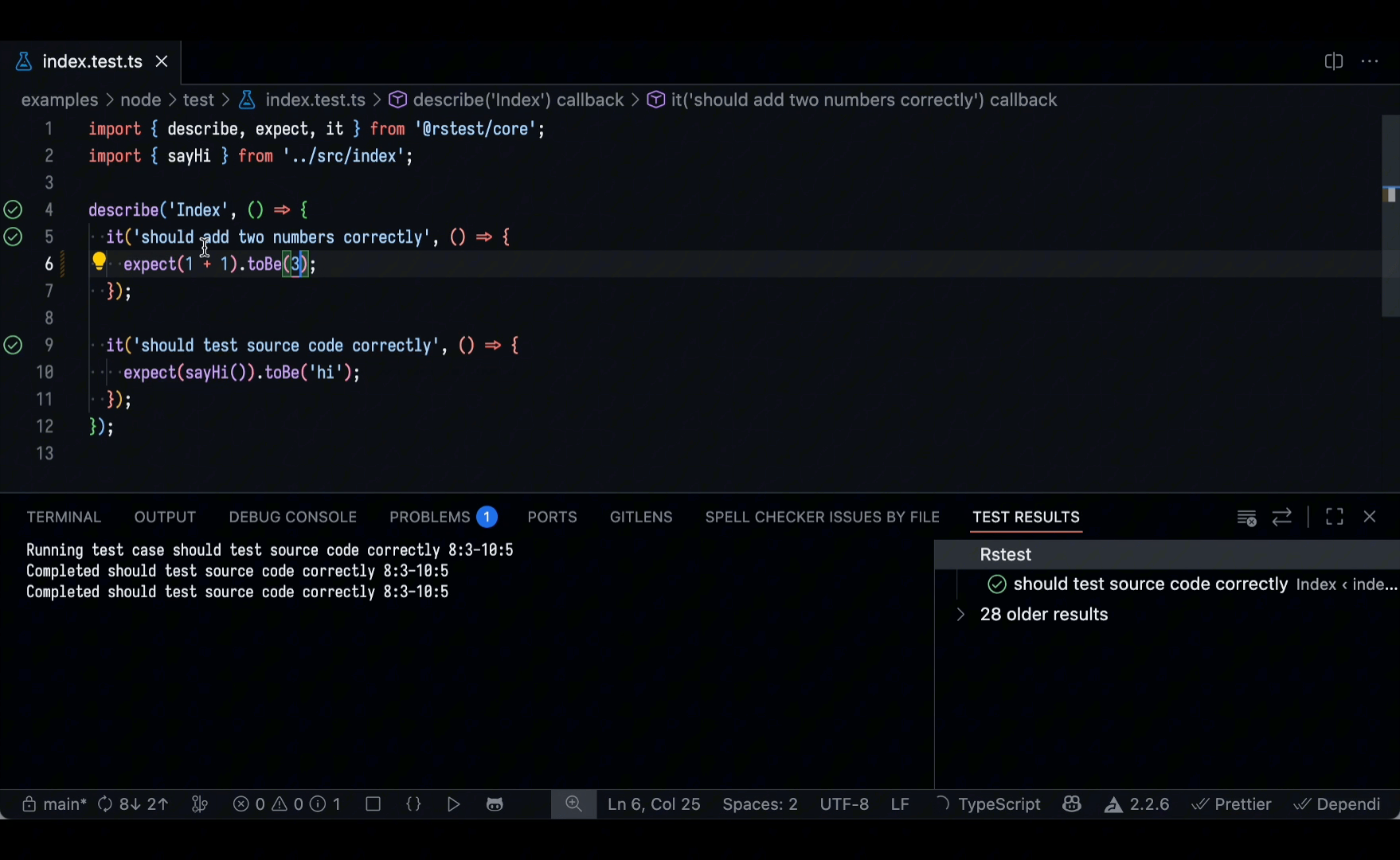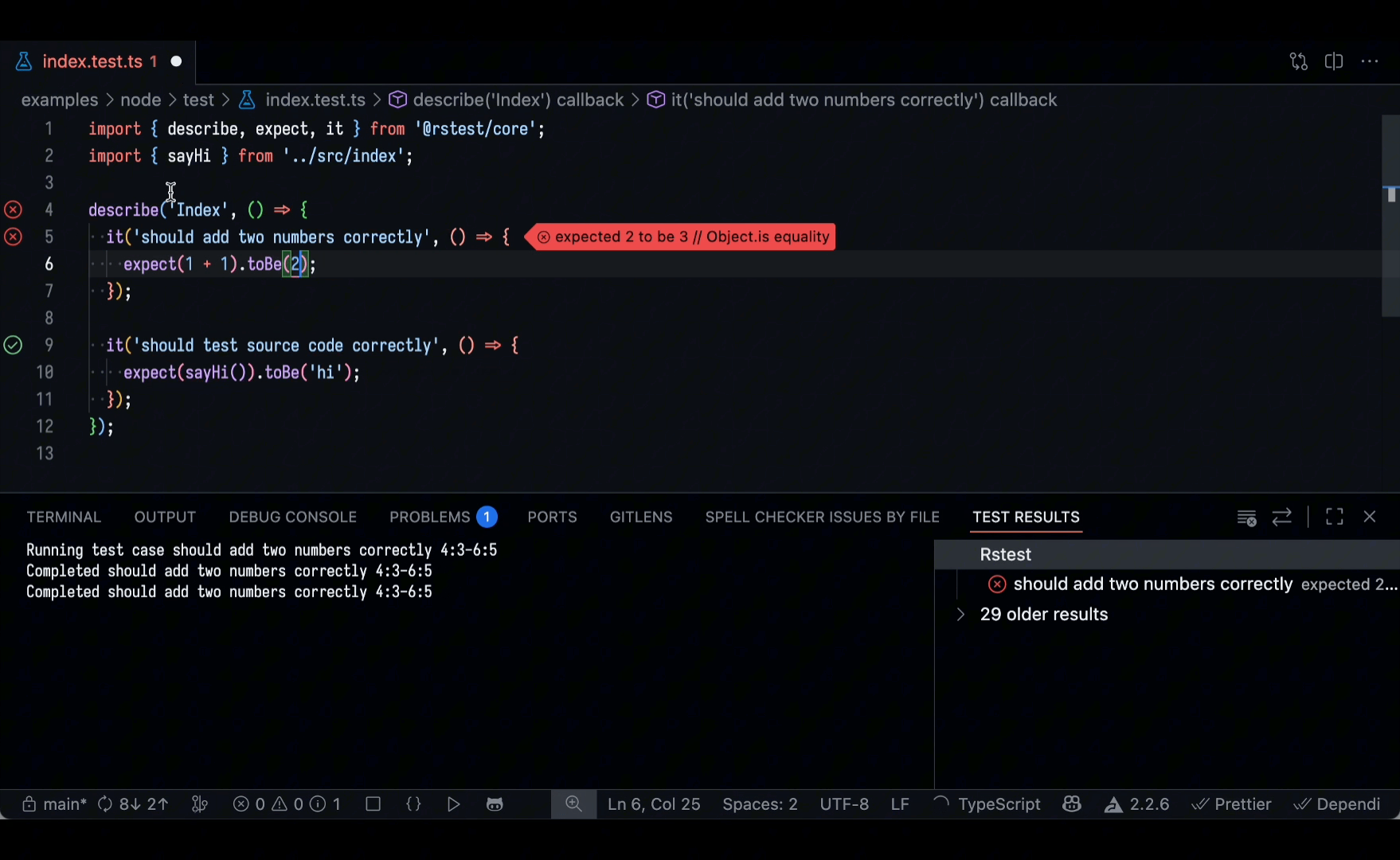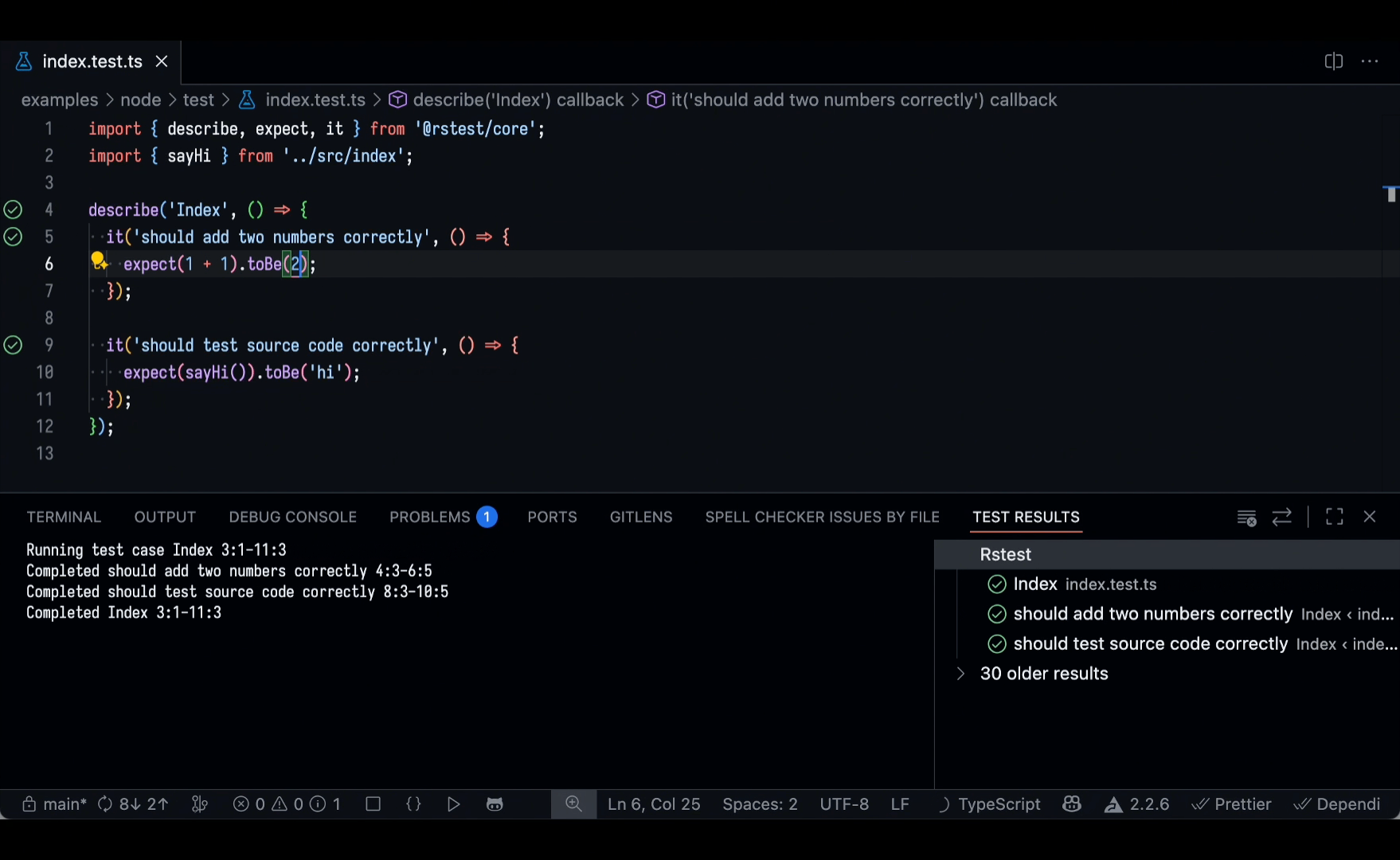
VS Code extension
The Rstest VS Code Extension is now available. It allows you to discover, run, and debug tests directly within the editor, helping you efficiently manage test cases and quickly review test results.
Coverage support
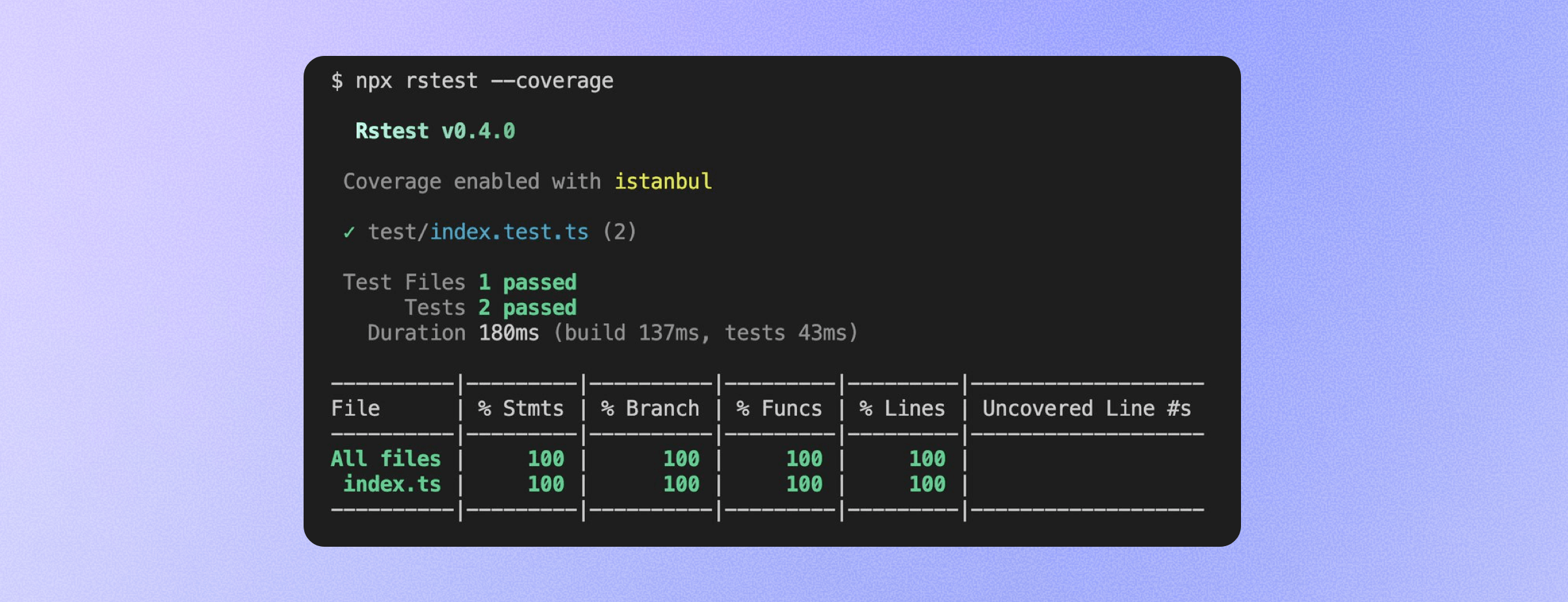
Rstest now supports collecting code coverage using Istanbul and generating detailed coverage reports. For more information, see Rstest – Coverage.
Rsdoctor 1.3
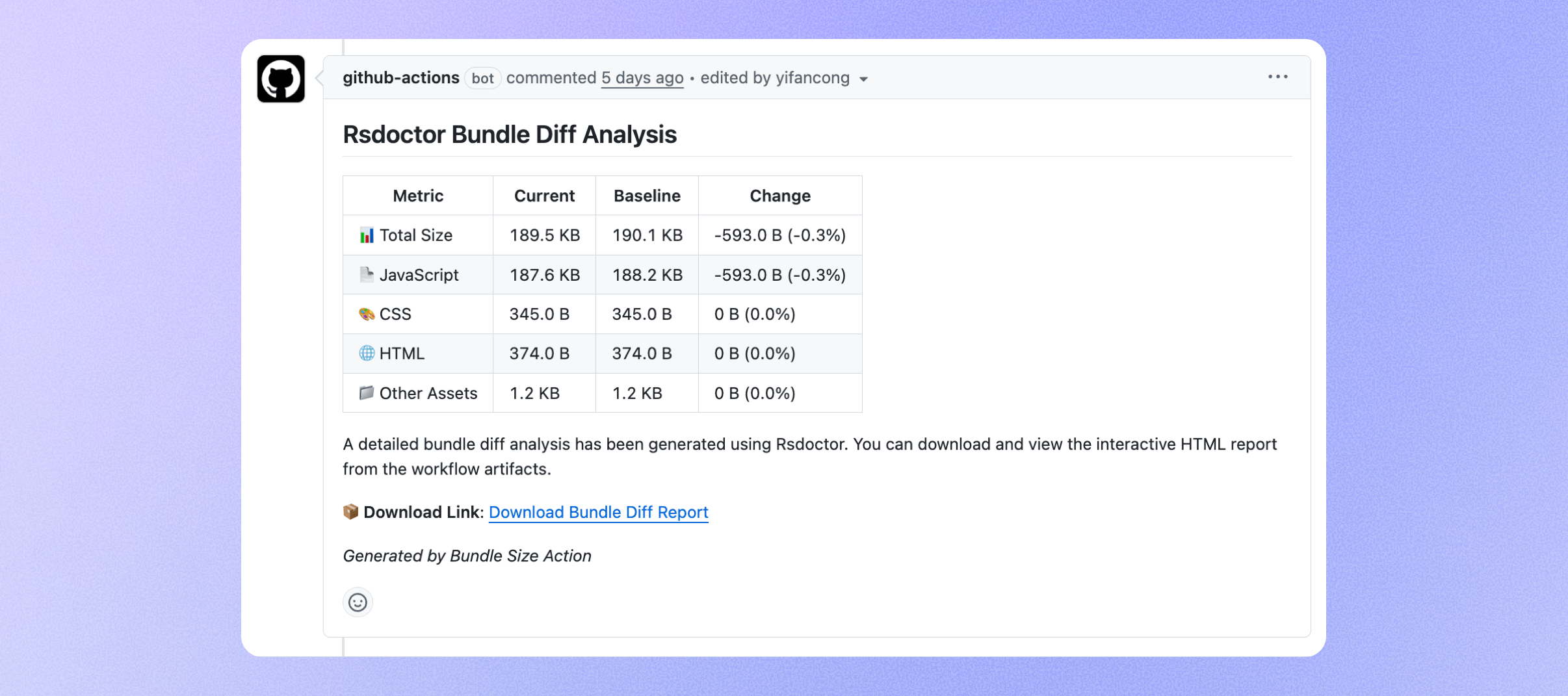
Rsdoctor GitHub Actions
Rsdoctor now provides a GitHub bundle diff action, which automatically detects and compares bundle size changes during the CI phase. This helps teams identify and prevent bundle size regressions early.
All-in-one JSON report
Rsdoctor now supports exporting a all-in-one JSON report file in Brief mode. This file can be easily stored, shared, or used for further data analysis. In addition, we’ve introduced a new Playground page, where developers can upload the JSON report to reopen and visually explore the analysis results.
Ecosystem
next-rspack
In Next.js 16, next-rspack has integrated Rspack's custom Rust binding solution, delivering significant performance gains:
- 24% faster build performance
- 10% faster dev performance
In this customized Rspack Rust binding, the externals logic from Next.js has been moved to the Rust side, greatly reducing communication overhead between JavaScript and Rust.
The benchmark is based on the chakra-ui-docs repository. Full performance data is available here: PERF.md.
Upgrade guide
Upgrade SWC plugins
If your project uses SWC Wasm plugins (such as @swc/plugin-emotion), you need to upgrade the plugins to a version compatible with swc_core@46, otherwise it may cause build errors due to version incompatibility.
For more details, see FAQ - SWC plugin version mismatch.
Remove experiments.layer
experiments.layer option has been deprecated, you can remove it directly:

