December 31, 2025
Announcing Rspack 1.7

We are excited to announce Rspack 1.7! This marks the final minor release in the Rspack 1.x series and focuses on stabilizing existing features. Next, we'll be moving toward Rspack 2.0.
Notable changes include:
- New features
- Rstack progress
New features
Improved SWC plugin compatibility
In previous versions, the upgrade cost for SWC Wasm plugins was relatively high. This was because the SWC AST structure evolved across versions, causing existing plugins to fail after an SWC upgrade. Plugin authors needed to adapt their plugins, and users needed to upgrade their dependencies in lockstep, which affected project stability and the upgrade experience.
To address this issue, we contributed a series of compatibility improvements to the SWC community, including:
- Using the self-describing cbor serialization scheme to replace the version-sensitive rkyv, allowing Wasm plugins to better adapt to AST structure changes.
- Introducing the
Unknownvariant for enum types in the AST, improving fault tolerance when encountering new fields or nodes.
In Rspack 1.7, we upgraded the SWC version in use and adopted these compatibility improvements. From now on, in most scenarios, SWC upgrades are unlikely to break existing plugins built with older SWC versions.
Currently, this approach has been adopted by most popular SWC Wasm plugins. If you are an SWC Wasm plugin author, refer to the official guide to adopt these changes and reduce maintenance costs in future version evolutions.
Importing assets as bytes
Rspack now natively supports the Import Bytes proposal for importing assets as bytes. You can now import assets as Uint8Array and decode them with TextDecoder.
Lazy compilation
In Rspack 1.5, we stabilized the Lazy Compilation feature and enabled it by default for dynamically imported modules in Rsbuild.
Starting from Rspack 1.7, the Rspack CLI also enables lazy compilation by default for dynamically imported modules when building web applications. This change reduces the number of modules in the initial build, thereby speeding up the dev server startup.
If you have special requirements, such as needing to debug the full build output or inspect the complete module graph, you can explicitly disable this feature by setting lazyCompilation to false.
Experimental features stabilized
In Rspack 1.7, we have stabilized several experimental features. The following capabilities have been verified in production and are now considered stable, and the corresponding experimental flags have been deprecated or enabled by default:
- Constant Inlining Optimization: This optimization is now stable and enabled by default in production builds.
- The original experiments.inlineConst option is deprecated.
- If you need to disable this behavior, use optimization.inlineExports to control it.
- TypeScript Enum Inlining Optimization: This optimization is now stable.
- The original experiments.inlineEnum option is deprecated.
- Use collectTypeScriptInfo.exportedEnum to control whether to collect exported
enuminformation. - Use optimization.inlineExports to control whether to inline
enum.
- Type Re-export Check: This optimization is now stable.
- The original experiments.typeReexportsPresence option is deprecated.
Refer to the Upgrade Guide to learn how to adjust related configurations.
Rstack progress
Rsbuild 1.7
Error overlay improvements
Rsbuild's error overlay now supports displaying runtime errors. When an exception is thrown during application execution, the error will be rendered directly on the overlay, helping you identify and diagnose issues faster.
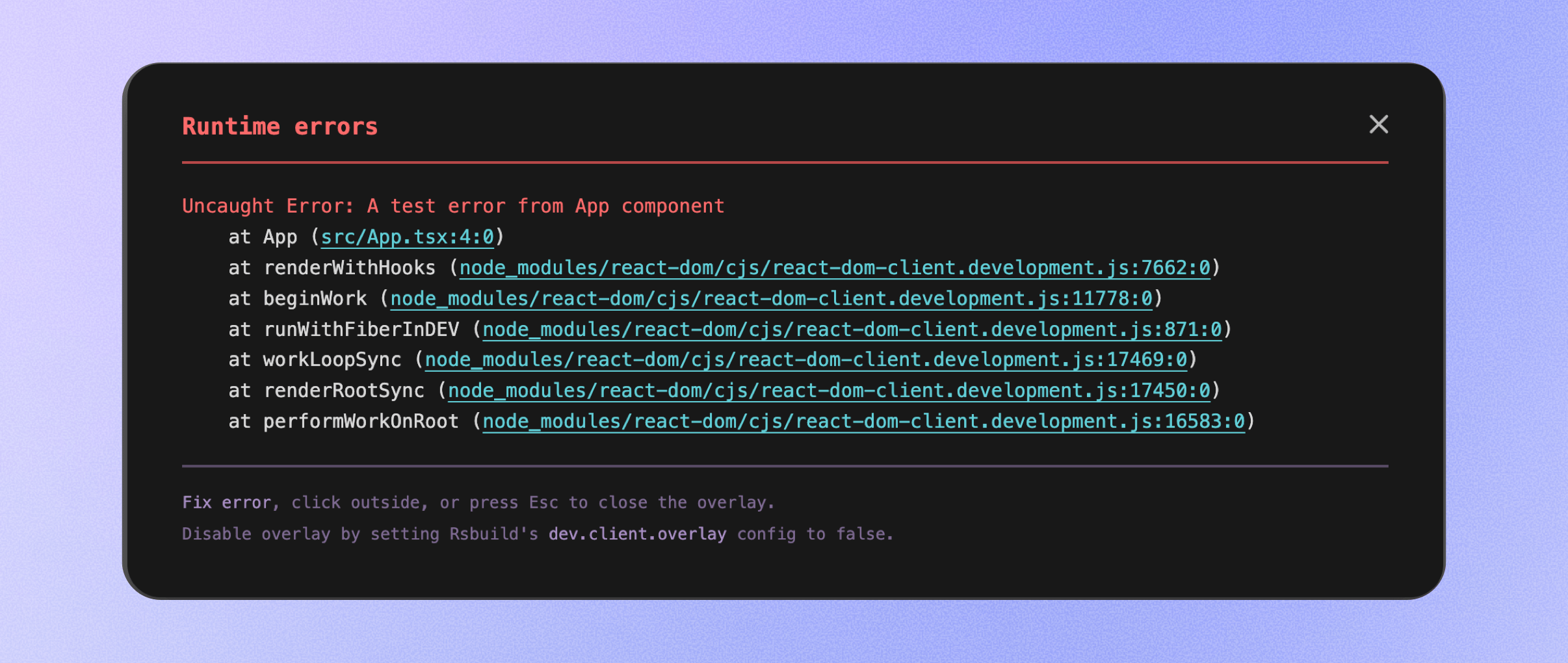
This feature is disabled by default and can be enabled via the dev.client.overlay.runtime option:
Asset size diff reporting
Rsbuild now supports reporting size differences to see whether the build output size has changed.

When the performance.printFileSize.diff option is enabled, Rsbuild records a snapshot of the asset sizes upon build completion. Subsequent builds will automatically compare with the previous result and display size deltas in the logs. You can clearly see whether each file has grown or shrunk, as well as the overall size change, making it suitable for quickly spotting size regressions during daily development.
create-rsbuild improvements
create-rsbuild now includes more out-of-the-box tools.
When creating an Rsbuild project, you can now choose to automatically integrate Rstest as the testing framework or enable Storybook for UI component development and debugging. Related dependencies and configurations will be set up during initialization, reducing repetitive manual configuration costs.
Rsdoctor 1.4
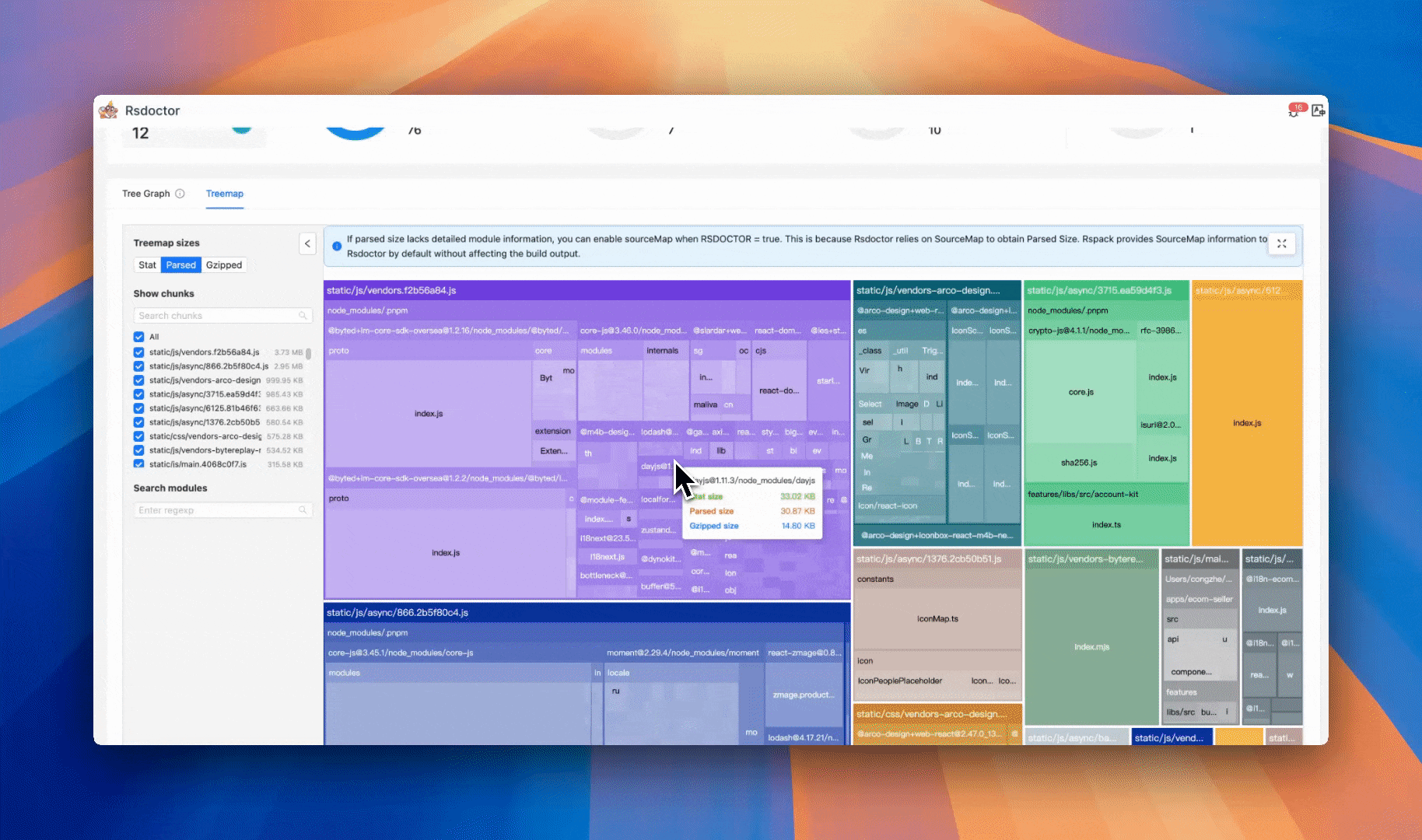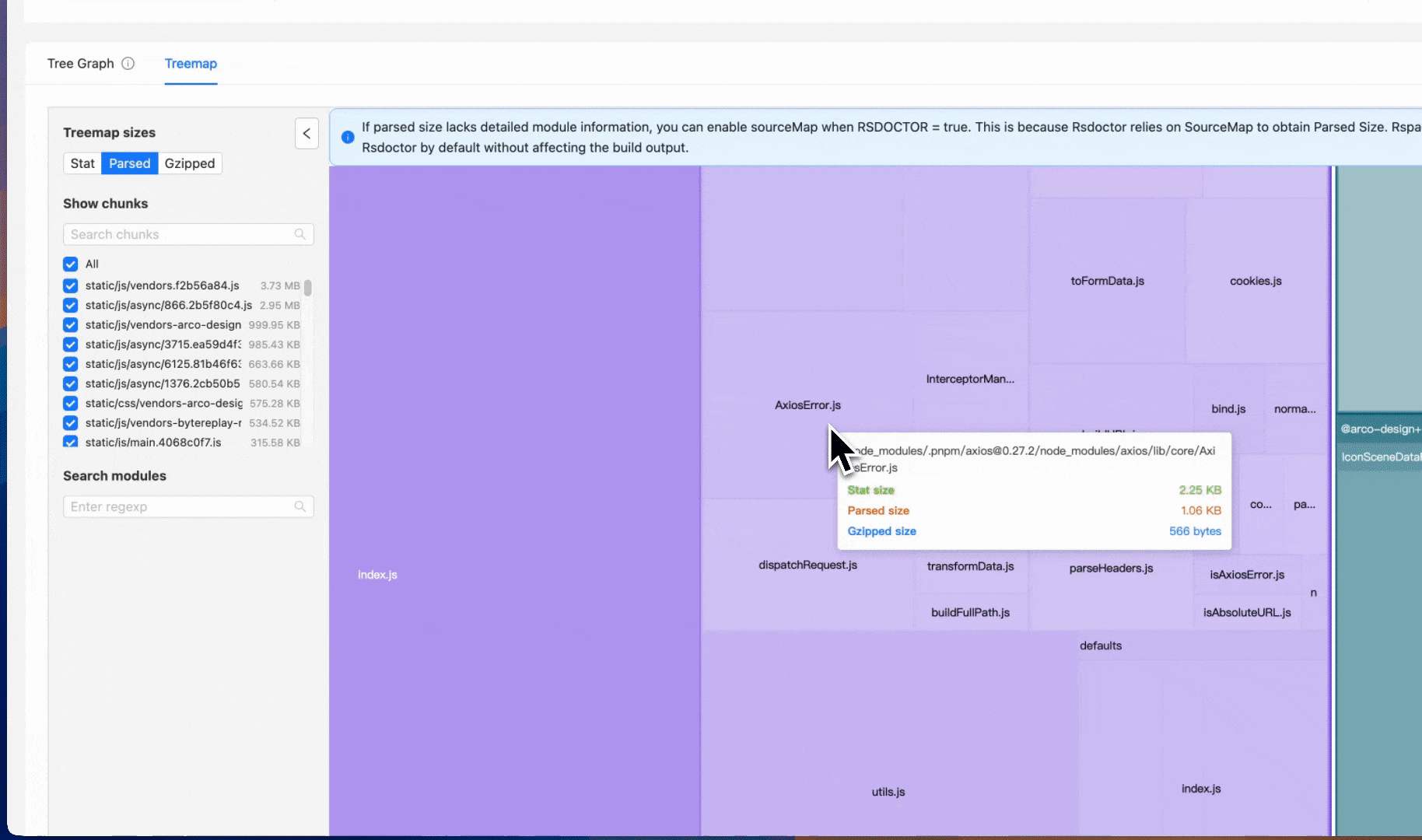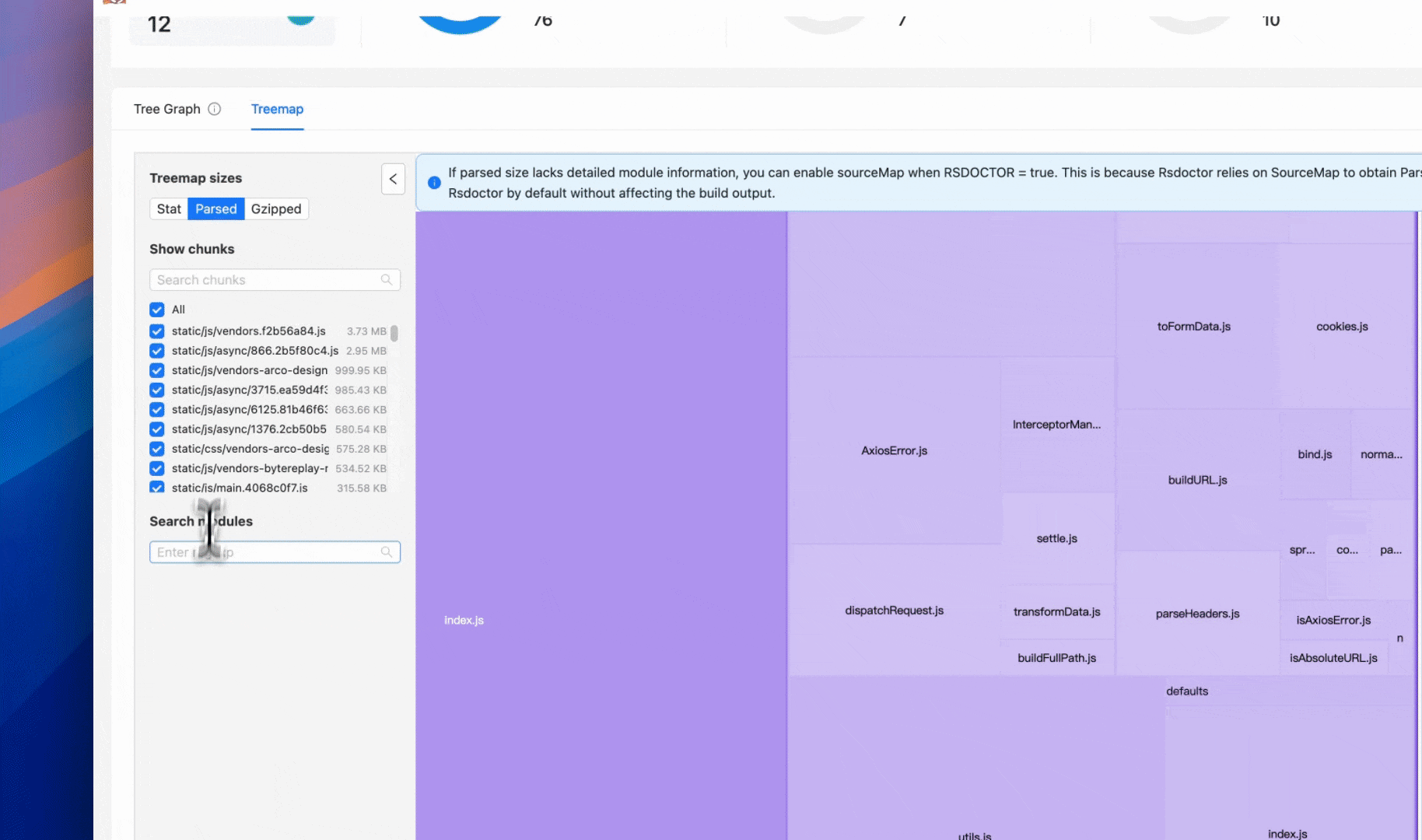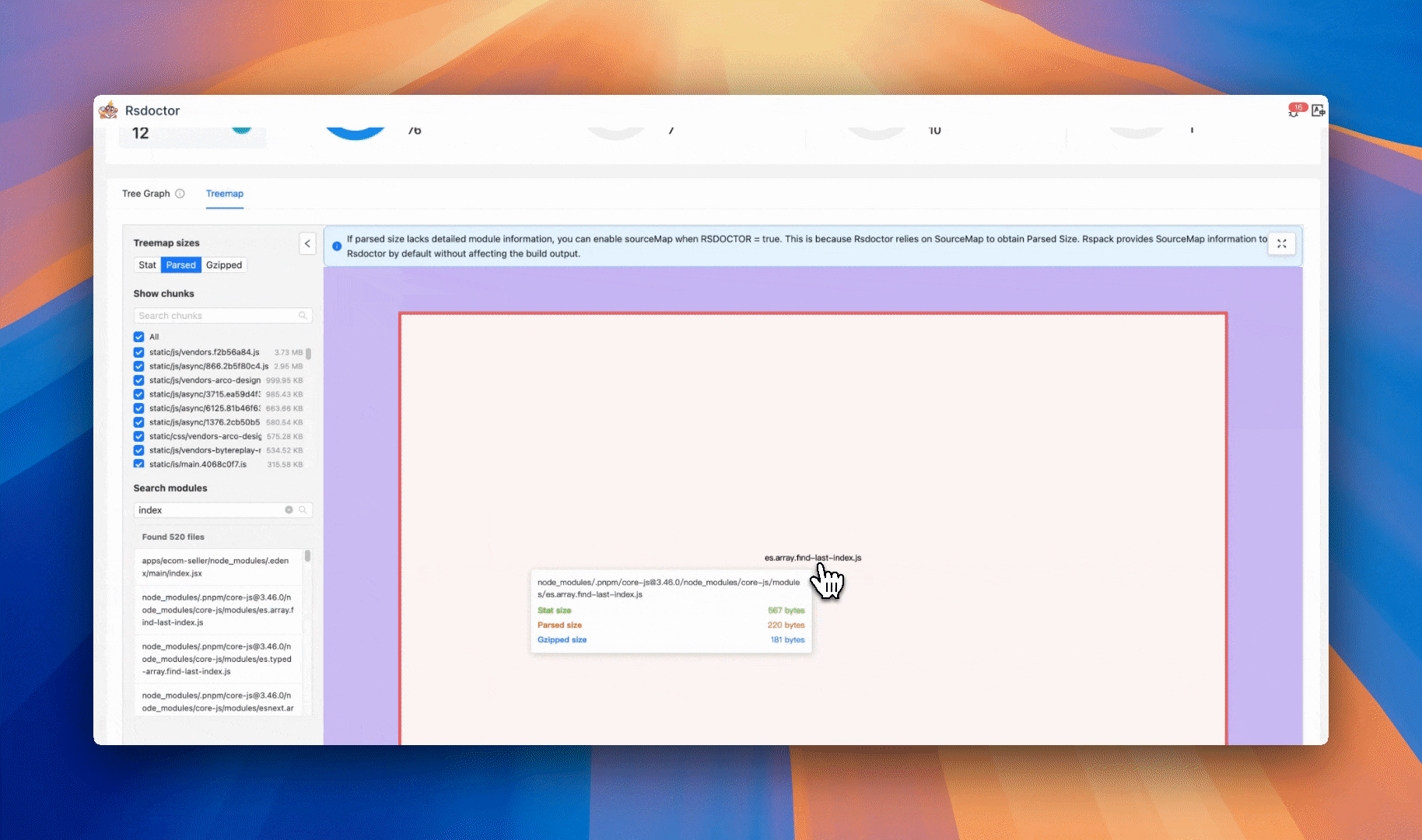
New treemap view
Rsdoctor 1.4 introduces an improved Treemap view. The new interaction design helps you analyze the overall composition of the bundle and the size proportion of various assets and modules more intuitively.
In this view, you can quickly locate specific modules or assets via search. Clicking on a module or asset will automatically focus and zoom in on the corresponding area. Double-clicking a module can also expand its dependency chain, allowing you to view the reference relationship between modules layer by layer, helping identify where the size comes from.
Rslib 0.19
ESM output stabilization
In previous versions, Rslib enabled Rspack's new ESM library output through the experimental configuration experiments.advancedEsm to improve the quality of ESM output. After verification and polishing over multiple versions, this capability is now stable.
Starting from Rslib 0.19, Rslib's bundle mode enables this feature by default. Developers do not need any additional configuration to directly obtain ESM artifacts that are friendly to static analysis and fully support code splitting.
JavaScript API
Rslib 0.19 introduces a JavaScript API, allowing developers to invoke Rslib's build capabilities programmatically in JavaScript code.
Here is a basic example:
For more usage, refer to the API Documentation.
Rstest 0.7
Configuration adapters
Rstest 0.7 introduces the extends option and an adapter mechanism, allowing you to directly reuse existing tool or framework configurations. An adapter is a configuration transformation function that can convert configurations from other tools into Rstest configurations, thereby reducing the integration overhead of Rstest.
For example, in a library project using Rslib, you can directly reuse the existing Rslib configuration via the @rstest/adapter-rslib adapter:
The adapter is responsible for converting configurations of different tools into Rstest configurations (such as define, alias, etc.), while extends is responsible for merging the converted configuration with Rstest's configuration. By combining the two, any tool or framework based on Rspack can be integrated with Rstest at minimal cost.
Currently, the @rstest/adapter-rslib adapter has been officially released, and we will launch more adapters to interface with various tools in the Rstack. You can also refer to Rstest - Adapters to write custom adapters.
Improved test feedback
Rstest has made several usability improvements for local development and debugging scenarios, making test feedback more intuitive:
-
Spot stuck tests earlier: Rstest now supports marking test cases that have not completed for a long time during local runs. When the test process slows down, you can directly see which case is executing and may be stuck, instead of waiting blindly for the test to time out.
-
Clearer timeout failure feedback: When a test fails due to timeout, Rstest now displays the number of executed assertions in the error message. This helps you quickly judge whether the test has been partially executed or is stuck in some asynchronous logic, thus locating the problem faster.
Rspress 2.0 RC
SSG-MD feature
In front-end frameworks that rely on dynamic React rendering, static information is often difficult to extract, and Rspress also encountered the same problem. Rspress allows users to enhance document expressiveness through dynamic features such as MDX fragments, React components, Hooks, and TSX routes. However, these dynamic contents face several challenges when converted to Markdown text:
- Directly inputting MDX to AI will contain a lot of code syntax noise and lose React component content.
- Converting SSG-generated HTML to Markdown often yields poor results, and information quality is difficult to guarantee.
To solve this problem, Rspress 2.0 introduces the SSG-MD feature. This is a new rendering mode, as the name suggests, the key difference from traditional Static Site Generation (SSG) is that it renders your page into Markdown files instead of HTML files, and generates llms.txt and llms-full.txt files. Compared to traditional approaches such as converting HTML to Markdown, SSG-MD has better information sources during rendering, such as React Virtual DOM, so it produces higher-quality static content with greater flexibility.
Enabling it is very simple:
The build will generate the following structure:
For custom components, you can control their rendering behavior in SSG-MD mode via environment variables:
This preserves the interactive experience of the document and helps AI understand the semantic information of the components.
For more details, refer to: SSG-MD Guide
Upgrade guide
Upgrade SWC plugins
If your project uses SWC Wasm plugins (such as @swc/plugin-emotion, etc.), upgrade the plugins to be compatible with swc_core@54 or above, otherwise build failures or runtime exceptions may occur due to version incompatibility.
For details, see FAQ - SWC plugin version mismatch.
Remove deprecated configuration
- The following experimental options have been deprecated and can be directly removed:
- Adjust the position of the collectTypeScriptInfo option in
builtin:swc-loader, removing therspackExperimentslevel:

